What is an example of MRP? Materials requirements planning, referred to by the initials MRP, is a technique which assists a company in the detailed planning of its production. Recall here that the master production schedulesets out an aggregate plan for production.

Material requirements planning (MRP) is a computer-based inventory management system designed to improve productivity for businesses. Companies use material requirements-planning systems to. Fishbowl is an inventory management platform that offers MRP, among other tools. Many users see Fishbowl as an affordable (albeit lighter-weight) alternative to NetSuite.
Standout features include QuickBooks integration, personalized customer support, and good reporting features. Or departments that became accustomed to hoarding parts in case of inventory shortages. You may also use them for service providers, such as job shops.
Examples of production environments include instances in which products are complex, products are only assembled to order, or demand items are discrete and dependent. It works by combining information from large national samples (for example tens of thousands of respondents) with ONS and census data. It consists of three primary steps: taking inventory of the materials and components on han identifying which additional ones are needed and then scheduling their production or purchase.
The aim is to allow each manufacturing unit to tell its supplier what parts it requires and when it requires them. The supplier may be the upstream process within the plant or an outside supplier. This added functionality also adds complexity, both in implementation and in operation. It is a material control system that attempts to keep adequate inventory levels to assure that required materials are available when needed.
After workers, employing more workers causes a fall in the marginal productivity – a classic example of diminishing returns. In this case, the marginal cost of labour is constant – £3a week. Receipts include production orders, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, open production orders, receiving stock transfer order, schedule lines, etc. New order proposals are not created until stock levels have fallen below the available portion of safety stock.
Lot size Procedures. Excel, and will also custom develop scheduling systems for them. Production-Scheduling. In order to apply this method it will be needed to know: 1. MRP EXERCISE 2nd Part.
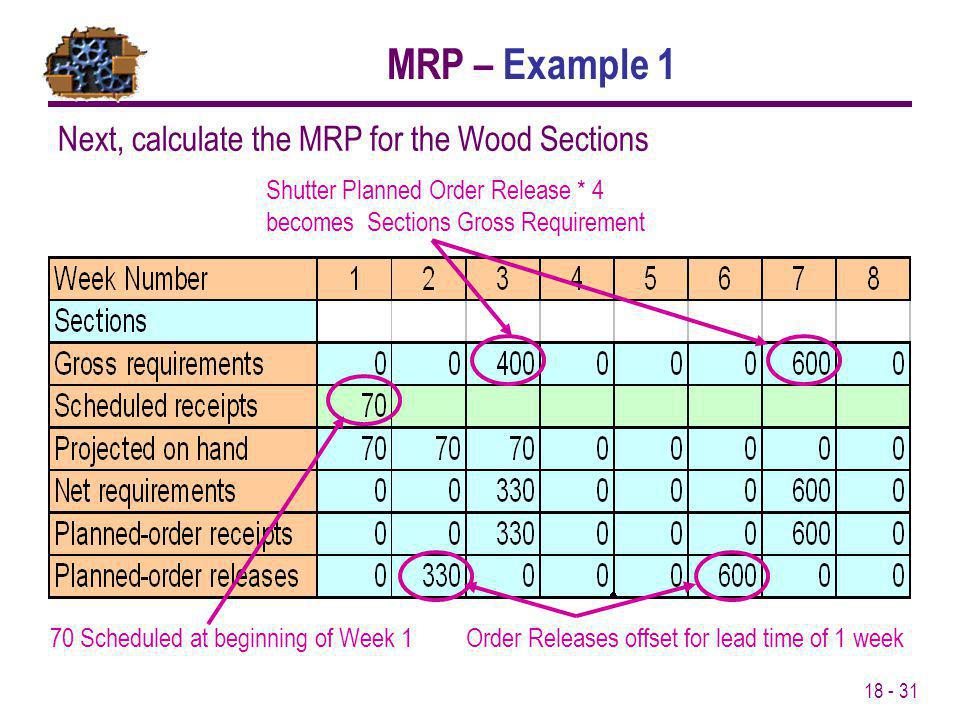
In the same way that ERP is doing this for large scale businesses. Any available stock is subtracte and lead times for the supply of components and the completion of finished products are estimated. It’s a methodology aimed at managing the whole quote-to-cash workflow process with the goal to improve the processes while the company grows.
Kanban keeps inventory costs down and. Role-Play in this definition refers to the typing RP done in video games, chatrooms and forums. The quantity-per (QP) defined in bill of service file is the load of the service.
Option 3: Asset Life Method 35. Where capital expenditure on an asset is financed wholly or partly by borrowing. I have tried with T code MD07. Please provide the T code if there is any.
In this example we will assume that one of the sites of your supply chain is using the Material Requirements Planning policy to timely replenish its inventory. They are planned using.

For example it may include an option for entering and invoicing sales orders (Sales Order Processing). Another common extension is into stock recording and a third into cost accounting.
The data required for these calculations are 1) bill-of-material structure, 2) external demands for end products 3) starting inventory levels (including planned order arrivals) and 4) planned lead times. Businesses typically manage their production planning with these systems, using them to forecast and order materials.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.